JY Electronics has launched the unidirectional deep snapback ESD product TT0311SA-Fx, specifically designed for the protection of high-speed signal lines.
The Development of Low Capacitance ESD
With the rapid growth of emerging industries such as 5G communications, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things, semiconductor process technology is advancing at an increasingly faster pace, and the sensitivity of ICs is also increasing. This has led to a higher level of demand for electrostatic protection. Concurrently, in the field of electrostatic protection for high-speed signal transmission, the development of lower capacitance is a primary direction. This is because excessive capacitance can cause signal loss during transmission, and large capacitance can also lead to longer charging and discharging times, reducing the switching speed of the device. This requires ESD protection devices to develop in the direction of low capacitance.
Advantages of Unidirectional ESD Protection

Unidirectional signals refer to signal lines that only exhibit positive or negative voltages. Generally, either unidirectional or bidirectional TVS can be selected. Typically, engineers prefer to use bidirectional TVS for the following reasons:
1.The use of bidirectional TVS avoids directional issues;
2.Under the same packaging, bidirectional TVS can achieve lower capacitance values compared to unidirectional TVS, especially in scenarios requiring high-speed signal transmission, where TVS with lower capacitance is demanded.
Comparison between Unidirectional and Bidirectional TVS
However, in some unidirectional signal transmissions, using bidirectional TVS may not provide the best protection effect, as bidirectional TVS only starts to conduct when both positive and negative voltages reach the breakdown voltage. At positive voltages, the conduction characteristic curves of unidirectional TVS and bidirectional TVS are similar. But at negative voltages, unidirectional TVS will forward conduct at about -0.7V, while bidirectional TVS need to reach the negative breakdown voltage to conduct (for example, the VBR of a 5V TVS is about -6V). At this point, since the main chip is often of a higher process, the I/O protection circuit is very fragile, which can cause the internal substrate diodes of the main chip to conduct first and burn out, leading to damage to the main chip.
Furthermore, when comparing unidirectional TVS and bidirectional TVS with the same packaging, it is found that the clamping voltage of unidirectional TVS is superior to that of bidirectional TVS. This is because, under the condition of the same chip area, bidirectional TVS requires more elements and a more complex structure. Unidirectional TVS, on the other hand, can maximize the area of the protection element, effectively reducing the clamping voltage and dynamic on-resistance, and enhancing the protection performance.
The Industry’s Lowest Capacitance Unidirectional Deep Snapback ESD Product TT0311SA-Fx
In response to the above issues, the R&D department of JY Electronics has overcome all difficulties and solved technical challenges. Aimed at high-speed signal transmission line applications such as USB 3.X and USB 4.0, they have developed the industry’s lowest capacitance unidirectional deep snapback type ESD electrostatic protector – TT0311SA-Fx, with an extremely low capacitance value of 0.24pF and a deep snapback voltage of 3V, which is the lowest capacitance among current industry unidirectional single-path products. After the voltage trigger of the deep snapback type ESD, it will instantly reduce the clamping voltage at both ends of the ESD. Under the same Ipp current, the Vc clamping voltage of the deep snapback type ESD is more than 30% lower than that of conventional ESD devices (currently, in the test requirements of telecom equipment manufacturers such as Huawei, the anti-static ESD sweep characteristic has been specifically emphasized).
At the same time, TT0311SA-Fx also has the electrostatic protection capability of air 15kV and contact 14kV according to the IEC61000-4-2 test level. These excellent performances enable TT0311SA-Fx to provide strong electrostatic protection for the backend IC and the entire circuit.
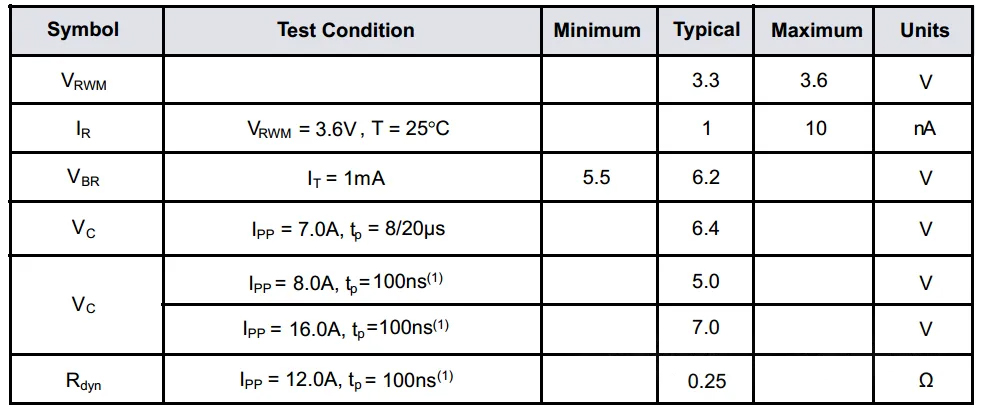
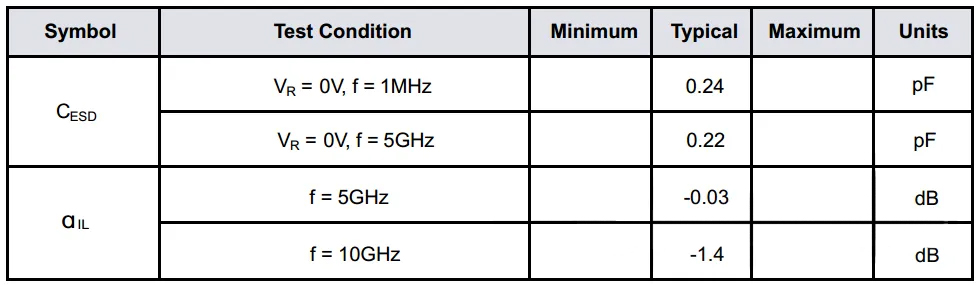

TT0311SA-Fx Datasheet
Notes on ESD for USB High-Speed Interfaces

For USB 3.X and USB 4.0 high-speed interfaces, consider the following points when selecting ESD/EOS protection components:
1.To ensure the integrity of high-speed signals transmitted via USB 3.X and USB 4.0, it is necessary to use ESD protection components with low capacitance.
2.High ESD voltage endurance is crucial, with a minimum requirement to withstand the ESD shocks from 8kV contact discharge as specified in IEC 61000-4-2.
3.A low clamping voltage is advantageous for better protective performance.
Layout Design Considerations
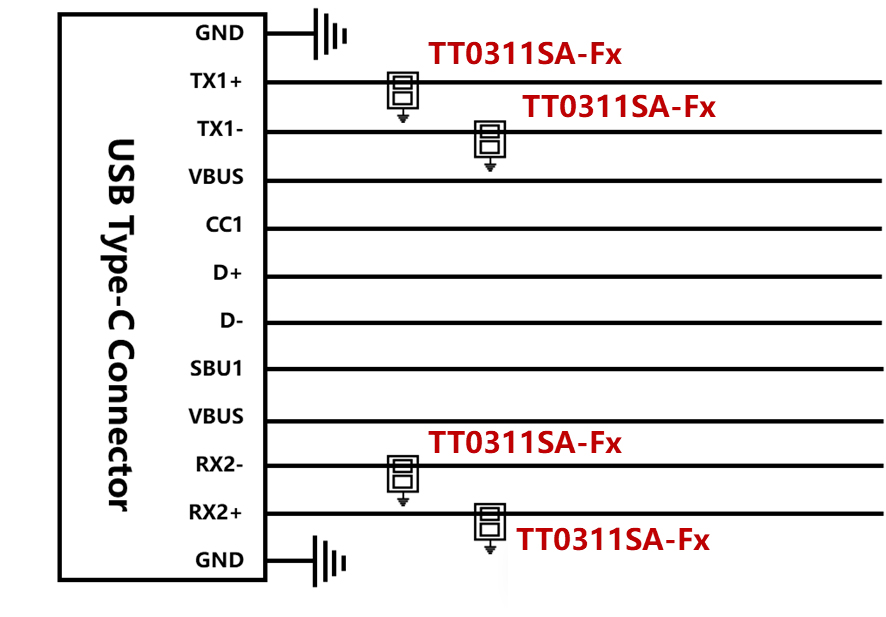
1.Place ESD protection devices as close as possible to I/O connectors to minimize ESD grounding paths and enhance protection performance.
2.In USB 3.X and USB 4.0 applications, ESD protection devices should be placed between the AC-coupling capacitors in the TX differential channel and the I/O connectors, so that no direct current can flow through the ESD protection devices, thus preventing any potential latch-up risks.
3.Use bent traces whenever possible to avoid unnecessary reflections.
4.Maintain equal trace lengths between the positive and negative lines of differential data channels to prevent the generation of common mode noise and impedance mismatch.